Air pollution represents one of the biggest risks to public health worldwide.
Pratite zagađenje zraka u svom gradu uz pametne senzore
Hundreds of thousands of people in Europe, and more than 7 millions globally, die prematurely every year because they have been exposed to concentrations of pollutants above the levels recommended by the World Health Organisation (WHO).
Why?
Why should YOU
Monitor Air?
Many studies have linked poor indoor air quality in schools to a variety of harmful
outcomes, including:
Poor indoor air quality in schools and kindergartens can have significant effects on both children’s health and
academic performance.
Here are some key points below:
By reducing air pollution,
communities can reduce
strokes, heart disease, lung
cancer and chronic and acute
respiratory diseases,
including asthma.
• To get relevant data on gases and
particles creating air pollution.
• To identify sources and pollution levels
• To be able to define necessary measures
to reduce air pollution.
• To save lives or make them better
Source:
EEA, European Environment Agency
Children are more prone to
the adverse effects of air
pollution. There are many
ways how pollution affects
them:
• Low birth weight
• Asthma and reduced lung function
• Risk of respiratory infections
• Upper respiratory infections and otitis
• Allergies, including allergic rhinitis
Source:
EEA, European Environment Agency
Act now and establish robust air quality monitoring
networks to track pollution levels and identify sources.
Which Pollutants
Should You Monitor?
By addressing both gaseous pollutants and particulate matter through comprehensive
strategies, we can significantly improve air quality and protect human health and the
environment.
Pollution subtances to track:
Gases
CO, SO2, NO,
NO2, O3, CO2
Particles
PM1, PM2.5, PM10
Particulate Matter (PM1, PM2.5 and PM10)
Tiny particles suspended in the air, which can penetrate the respiratory system and cause health problems.
Ozone (O3)
A gas that can cause respiratory issues and other health problems at ground level.
Nitrogen Oxide (NO)
Colorless gas and pollutant produced by combustion processes, such as those in vehicles and power plants.
Nitrogen Dioxide (NO2)
A pollutant primarily produced by vehicles and industrial activities, contributing to respiratory problems.
Sulfur Dioxide (SO2)
Emitted from fossil fuel combustion at power plants and other industrial processes, it can cause respiratory problems and other health issues.
Carbon Monoxide (CO)
A colorless, odorless gas produced by burning fossil fuels, which can be deadly in high concentrations.
Carbon Dioxide (CO2)
CO2 sensors measure the concentration of carbon dioxide in the air, which can indicate indoor ventilation effectiveness and occupancy levels.
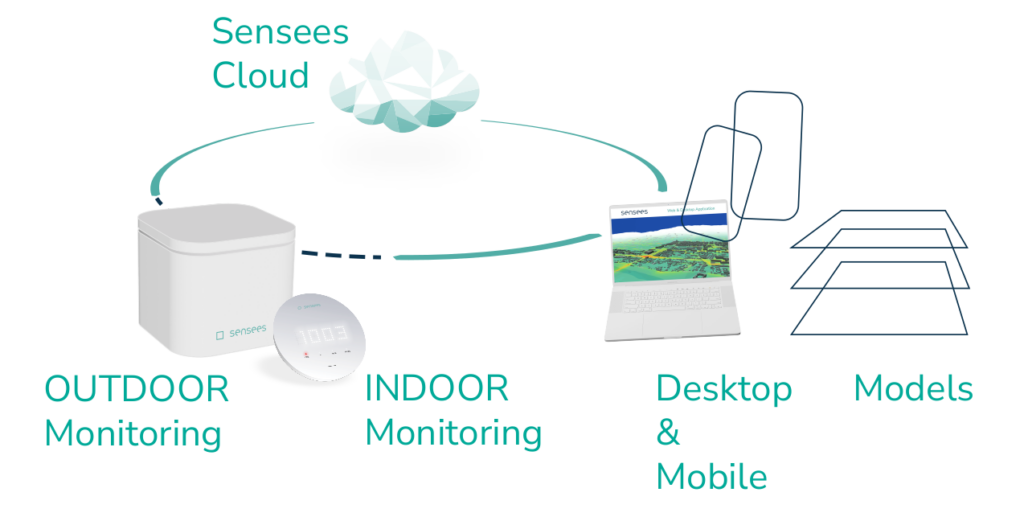
We Are Your Air Pollution Monitoring Partner!

OUTDOOR
Air Quality Monitoring System
We can help you mitigate pollution by monitoring and analyzing various gases and particulate matter that can have harmful effects on human health.
Sensees Outdoor Air Quality Monitoring System is a professional smart sensor platform for outdoor monitoring of multiple air quality and other environmental parameters like particulate matters (PMs), nitrogen oxides (Nox), noise or electromagnetic field levels in a city or rural setting, all the while providing real time data insights.
Electrochemical sensors used in measurements come factory-calibrated and undergo additional calibration and validation in
Smart Sense laboratory.
Gases:
CO, SO2, NO, NO2, O3, CO2
Particles:
PM1, PM2.5, PM10

Application Areas

Urban Air
Pollution
Monitoring
Used by city authorities to
monitor and manage air
pollution.
Read More

Indoor
Air Quality
Used in schools, kindergardens
and commercial buildings to
ensure a healthy indoor
environment.
Read More

Environmental
Research
Provides data on the impact of air
pollution on health and
helps in assessing the exposure
of populations to harmful
pollutants and implementing
health interventions.
Read More




